Air filters play a vital role in maintaining clean air quality and ensuring general health and safety. Air filters are designed to capture and remove airborne pollutants such as dust, pollen, smoke, and bacteria. They have been around for many years and have undergone numerous changes in design and technology. One can trace the history of air filtering back to ancient civilizations, where people used materials such as cloth, leaves, and animal skins to filter air. However, it wasn’t until the Industrial Revolution in the 19th century that air filters began to be used on a larger scale. Read More…
Duraflow Industries is the premier aftermarket and OEM supplier of various filtration products. We feature a complete line of filters for applications such as air scrubbers, absorption of thousands of organic compounds, drinking water filtration, and waste water abatement. Our just-in-time production techniques allow us to maintain production flexibility and meet fast turnaround times. From...

For more than 25 years, RoboVent's focus has been on the delivery of clean air and healthy environments in manufacturing facilities. This has earned us the leading position in the collection and filtering of airborne contaminants generated by metalworking and other industrial processes. We are passionate about providing clean air solutions to the industry, and this dedication to the cause brings...

Clean Liquid Systems is a leading manufacturer of air and liquid filters. Our number one priority is to create the best filters that match the needs of our customers. We strive to have a fast turnaround while not reducing the quality of our products. Filtration is the only thing we do and ensure that we make our products right. We provide our customers with hundreds of years of experience and...
Our world-class facilities set us apart from the competition. We work hard to make our customers happy with our air filters. We can provide what you need to keep your air clean in whatever industry you are in. Our goal is to exceed your expectations so you can focus on what you do best! Whether you need support in design, products, delivery, or support, we can supply it all!

At Hengst Air Filtration, we are driven by a passion for clean air and advanced filtration solutions that safeguard both people and equipment. We design and manufacture high-performance air filters that meet the demanding requirements of a wide range of industries, from automotive and heavy equipment to industrial facilities, cleanrooms, and HVAC systems.
MCR inventories a large stock of Cleanroom Fan Powered and Ducted Air Filters. The Mac 10 FFU is known for being the quietest filter available and has been tested below 5O dBA with a rated flow of 90 FPM. Its modular design fits conveniently into 2`x4` to 2x2 T-Bar drop ceilings, and with a low profile of less than 13" it permits installation into tight ceiling spaces. Contact our company today!
More Air Filter Manufacturers
Air filtration technology has evolved dramatically over the past century, becoming an indispensable part of modern living and industrial operations. The early 20th century saw the introduction of air filters in heating and ventilation systems, especially in healthcare facilities striving for cleaner, safer air. By the 1960s and 70s, growing awareness of air pollution and its impact on public health led to significant advancements in air filter technology. Today, air filters form the backbone of HVAC systems and are integrated into a diverse array of environments—from homes and offices to factories, cleanrooms, and vehicles. If you are searching for the right air filter manufacturer, explore leading suppliers in our directory to compare solutions tailored for your specific needs.
Air Filter Materials
The performance and efficiency of an air filter depend greatly on the materials used in its construction. Selecting the appropriate air filter material is crucial for achieving desired filtration levels, optimizing lifecycle costs, and ensuring compatibility with your HVAC or process system. Typical materials include fiberglass, activated carbon, and synthetic polymer fibers, each engineered to address specific contaminants and use cases.
- Fiberglass: Widely used in both residential and commercial HVAC systems, fiberglass air filters efficiently capture larger particles such as dust, pollen, and lint. These filters are economical and offer low resistance to airflow, helping maintain optimal system performance and reducing energy consumption. If you are searching for the best filter for general dust and allergen removal, consider fiberglass HVAC filters.
- Activated Carbon: Activated carbon air filters are engineered to remove odors, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), smoke, and other gaseous pollutants. By adsorbing molecules onto the carbon’s porous surface, these filters excel in air purifiers, industrial settings, and environments where odor and chemical control are essential. Wondering how to control odors in your commercial kitchen or lab? Activated carbon is often the answer.
- Synthetic Polymer Fibers: Filters composed of synthetic fibers such as polypropylene or polyester are ideal for environments demanding high levels of cleanliness—cleanrooms, hospitals, laboratories, and electronics manufacturing. These high-efficiency filters are optimized to capture microscopic particles, including bacteria and viruses, and are available in various filtration grades (MERV, HEPA, ULPA) to match application requirements.
Decision Factors When Choosing Air Filter Materials: When evaluating air filter materials, consider the following:
- Filtration Efficiency: What level of particle removal is required? This will determine if you need a basic pre-filter or a high-efficiency particulate air filter.
- Airflow Resistance: Materials with low resistance help maintain HVAC system efficiency and minimize energy costs.
- Lifespan and Maintenance: Some materials require frequent replacement, while others offer extended service life with periodic cleaning.
- Cost: Initial purchase price versus long-term operational costs, including maintenance and energy consumption.
- Application Suitability: Is the filter for residential, commercial, industrial, or cleanroom use? Each environment may have unique material requirements.
Other Noteworthy Air Filter Materials
The air filtration industry continues to innovate with new materials and composite media, each suited for specialized use cases:
- Aluminum Mesh Filters: Durable and reusable, ideal for commercial kitchens, exhaust hoods, and harsh industrial settings where grease, oil mist, or larger particulates are common.
- Pleated Paper Filters: A cost-effective solution for residential HVAC systems, offering moderate efficiency for dust and allergen capture. Curious which filter is best for allergies? Pleated paper filters are often recommended.
- Eco-Friendly Cellulose Filters: Made from plant-based fibers, these filters are biodegradable and suitable for environmentally conscious applications in both residential and commercial spaces.
- Silica Gel Filters: Used as desiccant media to control humidity and prevent mold growth, often found in industrial and electronics applications.
- Zeolite Filters: These highly porous materials excel at adsorbing gases, odors, and certain chemicals, making them useful for specialty industrial and laboratory settings.
- Carbon-Impregnated Filters: Combining activated carbon with other filter materials, these filters address both particulate and gaseous contaminants in a single element.
- Metal Oxide-Coated Filters: Filters treated with photocatalytic coatings such as titanium dioxide use UV light to catalyze the breakdown of harmful volatile organic compounds, enhancing air purification in advanced HVAC or air cleaner systems.
How Are Air Filters Manufactured?
Answer: The air filter manufacturing process combines material science, engineering precision, and stringent quality control to deliver reliable filtration products. The steps outlined below highlight how leading manufacturers create air filters for diverse markets, from standard residential HVAC filters to advanced HEPA and ULPA filters used in critical environments.
- Material Selection
- Filter Media: The filter’s core media is selected based on its intended application and required efficiency. Common options include:
- Cellulose (Paper): Used in pleated air filters for HVAC and automotive applications, offering cost-effective dust and particle retention.
- Synthetic Fibers (Polyester/Polypropylene): Chosen for durability and resistance to moisture, especially in industrial and commercial air filtration systems.
- Glass Fibers: Integral to HEPA and ULPA filters, glass fibers can capture up to 99.999% of particles as small as 0.1 microns, meeting the strictest cleanroom standards.
- Activated Carbon: Incorporated for the adsorption of odors, gases, and VOCs in specialized applications.
- Frame Materials: Structural frames are fabricated from cardboard (for disposable filters), aluminum, or durable plastics, ensuring stability and compatibility with installation environments.
- Filter Media: The filter’s core media is selected based on its intended application and required efficiency. Common options include:
- Media Preparation
- Cutting and Pleating: Filter media are precisely cut and pleated to increase surface area, which enhances dust-holding capacity and improves filtration efficiency. The pleat design is optimized for the target airflow and pressure drop.
- Impregnation (Optional): Certain filters are treated with antimicrobial agents, flame retardants, or hydrophobic coatings to bolster performance and safety.
- Assembly
- Framing: The prepared media is mounted in a frame, with spacers or support grids to maintain uniform pleat separation for optimal airflow.
- Sealing: Edges are sealed using adhesives or gaskets, preventing air bypass and ensuring all air passes through the filter media—a critical step for HEPA and ULPA filters.
- Layering: Multi-stage filters may combine several layers (e.g., a pre-filter, carbon layer, and HEPA media) to address a wider spectrum of contaminants.
- Reinforcement
- Support Grids: Metal or plastic mesh support is added to prevent media collapse, especially in high-velocity or high-pressure systems.
- Edge Banding: Additional reinforcement—such as tape or secondary frames—is applied for filters destined for demanding industrial or commercial environments.
- Quality Control and Testing
- Leak Testing: Filters undergo pressure or particle penetration tests (such as DOP or PAO testing for HEPA/ULPA filters) to ensure seal integrity and consistent performance.
- Efficiency Testing: Particle capture rates and airflow resistance are validated according to standards like MERV (Minimum Efficiency Reporting Value) or ISO 16890.
- Visual Inspection: Final checks verify that pleats, frames, and seals are free from defects that could compromise air quality or system function.
- Packaging
- Finished filters are sealed in protective packaging to prevent contamination during shipping and storage, labeled with sizing, efficiency rating, and application specifications.
Advanced Manufacturing Techniques
- Automation: High-volume filters, such as automotive or residential HVAC filters, are mass produced using automated cutting, pleating, and assembly lines, delivering consistent quality at scale.
- Manual Assembly: Specialty filters, such as custom-sized HEPA or ULPA filters for cleanrooms, may be assembled by hand to meet unique specifications and stringent tolerances.
- Cleanroom Manufacturing: The production of HEPA and ultra-fine filters often takes place in controlled environments to prevent contamination and uphold performance standards.
Are you considering manufacturing your own air filters, or do you need custom filter solutions? Contact leading air filter manufacturers to discuss capabilities and request quotes tailored to your requirements.
Types of Air Filters
Understanding the different types of air filters is vital for selecting the right filtration solution for your application. Below, we outline the most common air filter types and their ideal use cases. If you’re not sure which filter is best for your needs, start by asking: What contaminants are you targeting? What efficiency level is required? What are the air volume and pressure constraints of your system?
- Electrostatic Filters: These filters use an electrical charge to attract and capture airborne particles, offering enhanced removal efficiency over conventional passive filters. Electrostatic designs are popular for reusable air filters in both home and commercial air purification systems, as they can be washed and reused, reducing long-term costs.
- HEPA Filters: High-Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) filters trap at least 99.97% of airborne particles down to 0.3 microns. They are essential in healthcare, cleanroom manufacturing, and environments where the highest levels of particulate control are required—such as pharmaceutical labs and semiconductor fabs. Curious about how HEPA filters compare to other filtration technologies? Explore our HEPA vs. ULPA filter guide.
- HVAC Filters: HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) filters are critical in both residential and commercial buildings. These filters improve indoor air quality, protect HVAC system components, and contribute to energy efficiency by capturing dust, allergens, pet dander, and other airborne contaminants. Looking for the best HVAC filter for allergies, dust, or pet hair? Compare filter ratings such as MERV and filter materials to find the optimal fit for your system.
- ULPA Filters: Ultra-Low Particulate Air (ULPA) filters provide even finer filtration than HEPA, capturing at least 99.999% of particles as small as 0.1 microns. These filters are indispensable in critical environments like semiconductor manufacturing, pharmaceutical production, and biosafety labs, where even the tiniest particulate contamination can cause costly defects.
- Inline Filters: Inline filters are used in compressed air and pneumatic systems to remove oil mist, water, and particulates, ensuring clean air for industrial equipment and sensitive tools. If you’re facing frequent equipment maintenance issues, upgrading to a high-quality inline filter may improve air purity and system reliability.
- Exhaust Filters: Exhaust filters are designed to purify engine or process exhaust streams by capturing particulate matter and hazardous gases. Widely used in vehicles, industrial machinery, and generator sets, these filters help companies meet environmental regulations and reduce their carbon footprint.
- Foam Filters: Foam air filters are common in water filtration (such as aquariums and hydroponic systems) and in some automotive and small engine applications. Their porous structure enables effective capture of debris and particulates, while maintaining high airflow rates.
- Air Compressor Filters: These specialized filters remove water, oil, and dust from compressed air, protecting pneumatic tools and downstream equipment. High-quality air compressor filters are essential in automotive workshops, manufacturing plants, and any facility reliant on clean, dry compressed air.
Limitations of Air Filters
While air filters deliver clear health and operational benefits, understanding their limitations is essential for setting realistic expectations and optimizing air quality management strategies.
- Airflow Restriction: As air passes through a filter, especially high-efficiency models, resistance is introduced. Excessive pressure drop can reduce system efficiency and increase energy costs. Are you concerned about airflow in your HVAC system? Choose filters with a suitable MERV rating balanced for both filtration and airflow.
- Maintenance Requirements: All air filters require periodic inspection, cleaning, or replacement. Clogged or overloaded filters lose effectiveness, impede airflow, and may strain HVAC equipment, leading to higher operational costs and potential equipment failure.
- Limited Gas and Odor Removal: Standard particulate filters (fiberglass, pleated paper) are ineffective at removing gases, odors, and VOCs. For these pollutants, consider activated carbon filters or advanced photocatalytic filters.
- Filter Lifespan: Some filters need replacement monthly, while others last six months or longer. Lifespan is influenced by filter type, material, and environmental conditions. How often should you change your air filter? Check manufacturer recommendations and monitor filter condition regularly.
Proactive maintenance and an understanding of your specific air quality challenges are key to maximizing filter performance and minimizing limitations.
Benefits of Air Filters
The benefits of air filters extend well beyond simple dust control. Here are the top advantages of using high-quality air filtration systems in various environments:
- Improved Indoor Air Quality: By trapping dust, pollen, mold spores, and allergens, air filters help reduce respiratory issues and create healthier living and working spaces.
- Equipment Protection: In HVAC systems, cleanroom environments, and industrial settings, air filters prevent dust and debris from damaging sensitive equipment, extending system life and reducing maintenance costs.
- Compliance with Regulations: Industrial air filters enable organizations to meet environmental and workplace safety standards, avoiding fines and ensuring a safe environment for workers and the public.
- Odor and Gas Control: Specialized filters (activated carbon, zeolite, or photocatalytic) remove odors, VOCs, and chemical fumes, enhancing comfort and safety in homes, offices, laboratories, and manufacturing plants.
- Reduced HVAC Energy Consumption: Properly selected and maintained filters help maintain efficient airflow, reducing the energy required to heat or cool a space.
- Enhanced Health in Sensitive Environments: In healthcare, pharmaceuticals, and cleanrooms, advanced filtration is essential to protect against airborne pathogens and particulate contamination.
Are you looking to improve indoor air quality or meet specific regulatory standards? Evaluate your facility’s unique needs and consult with trusted air filter suppliers for expert guidance.
Applications of Air Filters
Air filters play a pivotal role in maintaining air quality and supporting health, safety, and operational efficiency across numerous industries. Common applications of air filters include:
- Residential Buildings: HVAC systems in homes rely on air filters to reduce dust, pollen, pet dander, and other allergens, improving breathing comfort and reducing cleaning frequency.
- Commercial Facilities: Offices, retail spaces, hotels, and restaurants use air filters to provide cleaner air for employees, customers, and guests, supporting well-being and productivity.
- Industrial Operations: Factories, warehouses, and processing plants deploy advanced air filtration to protect workers from hazardous dust, fumes, and chemical vapors generated during production.
- Healthcare Environments: Hospitals, dental clinics, and laboratories rely on high-efficiency filters to control airborne bacteria, viruses, and contaminants, ensuring sterile conditions and patient safety.
- Transportation: Air filters are used in aircraft, trains, automobiles, and buses to maintain cabin air quality and protect mechanical systems from dust and pollutants.
- Cleanrooms and Laboratories: In microelectronics, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and biotechnology, ULPA and HEPA filters ensure ultra-clean environments where even microscopic contamination can be catastrophic.
- Food and Beverage Production: Airborne contaminants can compromise the quality and safety of food products. Specialized air filters protect product purity throughout the production process.
Are you seeking air filtration solutions for a specific industry or facility? Browse our directory of air filter manufacturers to find suppliers with expertise in your sector.
Choosing the Correct Air Filter
Selecting the right air filter is a critical step in achieving optimal air quality and system performance. Consider the following factors when evaluating air filtration options:
- Contaminant Profile: Identify the primary pollutants to control—dust, allergens, smoke, odors, VOCs, or microorganisms. This determines the appropriate filter type and efficiency rating.
- Filtration Efficiency: Match the filter’s performance (MERV, HEPA, ULPA ratings) to your application’s requirements. Higher efficiency filters capture smaller particles but may increase airflow resistance.
- System Compatibility: Ensure the filter fits your HVAC or air handling unit’s size and airflow specifications without causing excessive pressure drop.
- Maintenance Requirements: Factor in replacement intervals, cleaning procedures, and total cost of ownership. Some filters are washable or reusable, while others are disposable.
- Regulatory Compliance: For industrial, healthcare, or cleanroom applications, verify that your filter meets relevant standards and certifications.
- Budget: Weigh the initial cost against long-term expenses, including energy usage, filter replacement, and system maintenance.
Still unsure which air filter is best for your needs? Try asking:
- What MERV rating should I choose for allergy reduction in my home?
- Which air filter is most effective for controlling VOCs in a laboratory?
- How do I balance energy efficiency with filtration performance in a commercial building?
Consulting with HVAC professionals or air filtration experts can help you navigate specifications and select the optimal filter for your environment.
Choosing the Correct Air Filter Supplier
Finding a reliable air filter supplier is just as important as choosing the right filter. Here’s how our directory can help streamline your purchasing process:
- Comprehensive Supplier Profiles: Each supplier listing includes detailed information about their manufacturing capabilities, certifications, core industries served, and product portfolios.
- Easy Quote Requests: Use our RFQ (Request for Quote) form to contact multiple suppliers simultaneously, saving time when comparing pricing and capabilities.
- Preview Company Specializations: Our website preview tool allows you to quickly assess each supplier’s strengths—whether you need standard HVAC filters, custom HEPA solutions, or industrial air filtration systems.
- Direct Communication: Supplier profiles include contact forms for direct inquiries about pricing, product customization, lead times, and technical support.
Ready to start your supplier search? Compare top air filter manufacturers now to find the best partner for your air quality goals.
Explore More:
- Want to learn about HVAC filter types, ratings, and replacement schedules?
- Need guidance on cleanroom filtration solutions?
- Curious about emerging air purification technologies for homes, schools, or industrial settings?
Start your research or request a quote today!
What are the common materials used in air filter manufacturing?
Common air filter materials include fiberglass, activated carbon, synthetic polymer fibers such as polyester and polypropylene, aluminum mesh, pleated paper, eco-friendly cellulose, silica gel, zeolite, carbon-impregnated materials, and metal oxide-coated media. Each material targets different contaminants and application requirements.
How are air filters manufactured?
Air filters are manufactured through a process that includes material selection, cutting and pleating of the filter media, assembly of the media into frames, sealing for air-tightness, reinforcement for durability, rigorous quality testing for efficiency and air leakage, and secure packaging to prevent contamination. Techniques range from fully automated lines for large-scale production to hand assembly for custom or ultra-clean applications.
What are the main types of air filters and their applications?
The main types of air filters include electrostatic filters (for washable, reusable filtration), HEPA filters (high-efficiency particulate removal for healthcare and cleanrooms), HVAC filters (for dust and allergen control in buildings), ULPA filters (ultra-fine filtration for critical environments), inline filters (for compressed air systems), exhaust filters (for engines and industrial equipment), foam filters (for water and some engine applications), and air compressor filters (for clean, dry compressed air).
What factors should I consider when selecting an air filter?
Key factors to consider include the contaminants you need to control, the filtration efficiency required (MERV, HEPA, or ULPA rating), compatibility with your HVAC or air handling system, expected filter lifespan and maintenance requirements, regulatory compliance for your application, and your overall budget considering both upfront and long-term costs.
What are the limitations of air filters?
Air filters can restrict airflow, especially if they are high-efficiency models or become clogged from lack of maintenance. Standard filters may not remove gases, odors, or VOCs, which requires specialized materials like activated carbon. Filter lifespan varies and regular replacement or cleaning is essential to maintain performance and avoid equipment damage.
What are the benefits of using air filters?
Air filters improve indoor air quality by removing dust, allergens, and contaminants, protect sensitive equipment from particulate damage, help comply with health and environmental regulations, control odors and gases with specialized media, reduce HVAC system energy consumption, and ensure health and safety in sensitive environments like hospitals and cleanrooms.
How do I choose a reliable air filter supplier?
Choose suppliers with comprehensive profiles detailing manufacturing capabilities, certifications, and product offerings. Evaluate their experience across relevant industries, review customer testimonials, and use directory tools to request quotes and compare specializations directly. Direct communication can clarify customization options, lead times, and technical support.
What are the common applications of air filters?
Air filters are widely used in residential and commercial HVAC systems, industrial operations, healthcare settings, transportation (vehicles and aircraft), cleanrooms, laboratories, and food and beverage production facilities. Each application demands specific filter types and efficiencies to address unique air quality requirements and regulatory standards.
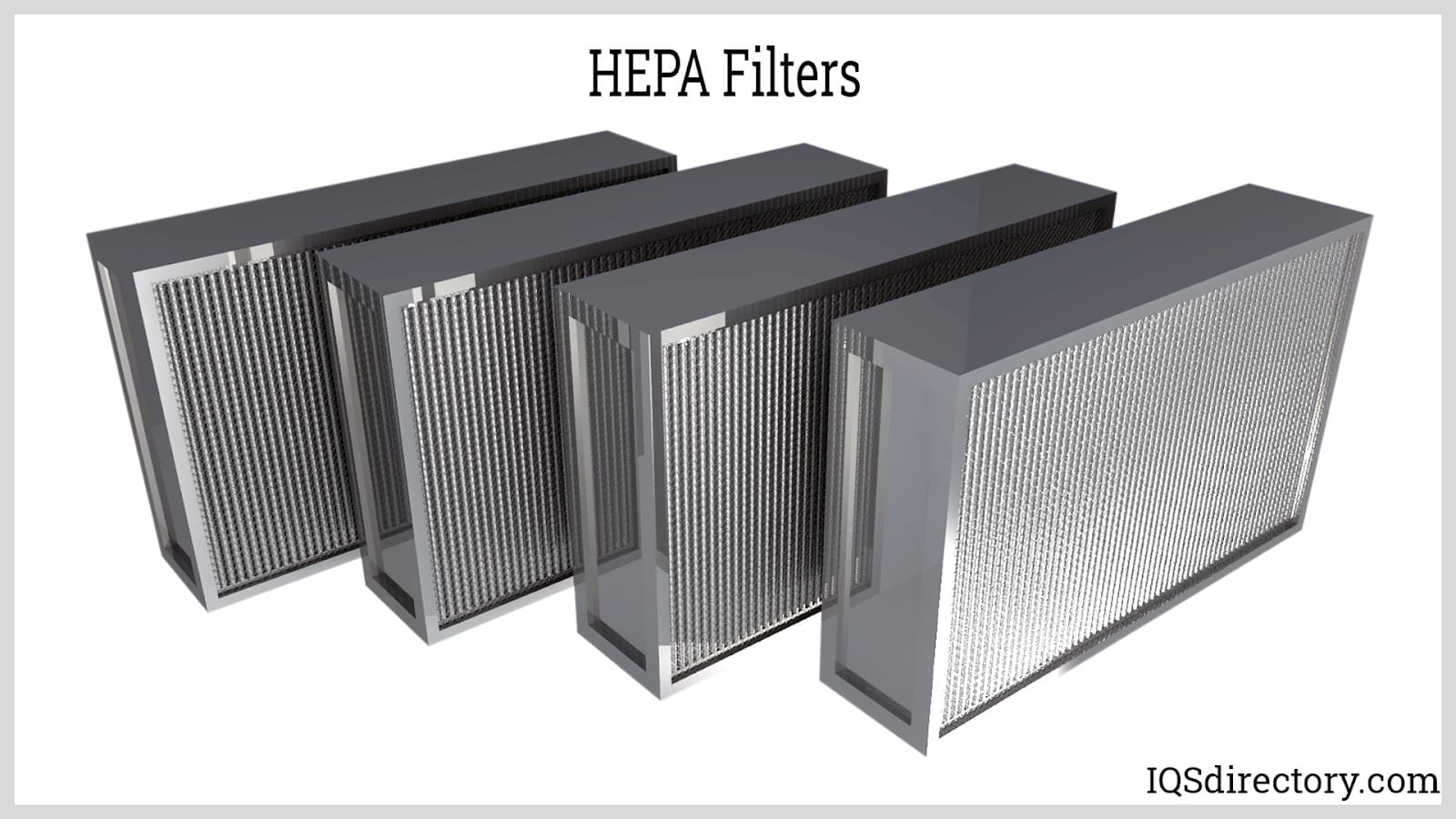
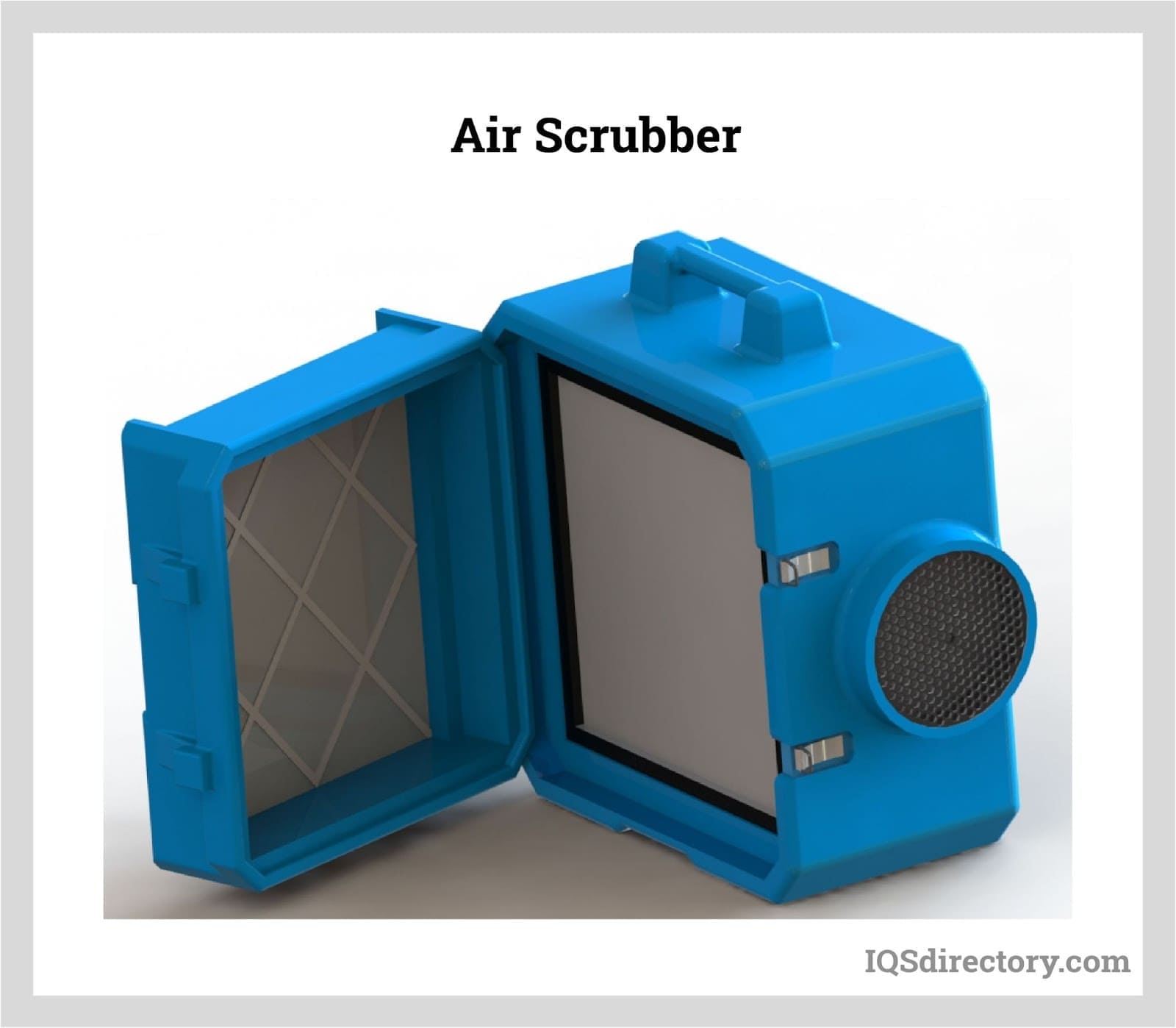

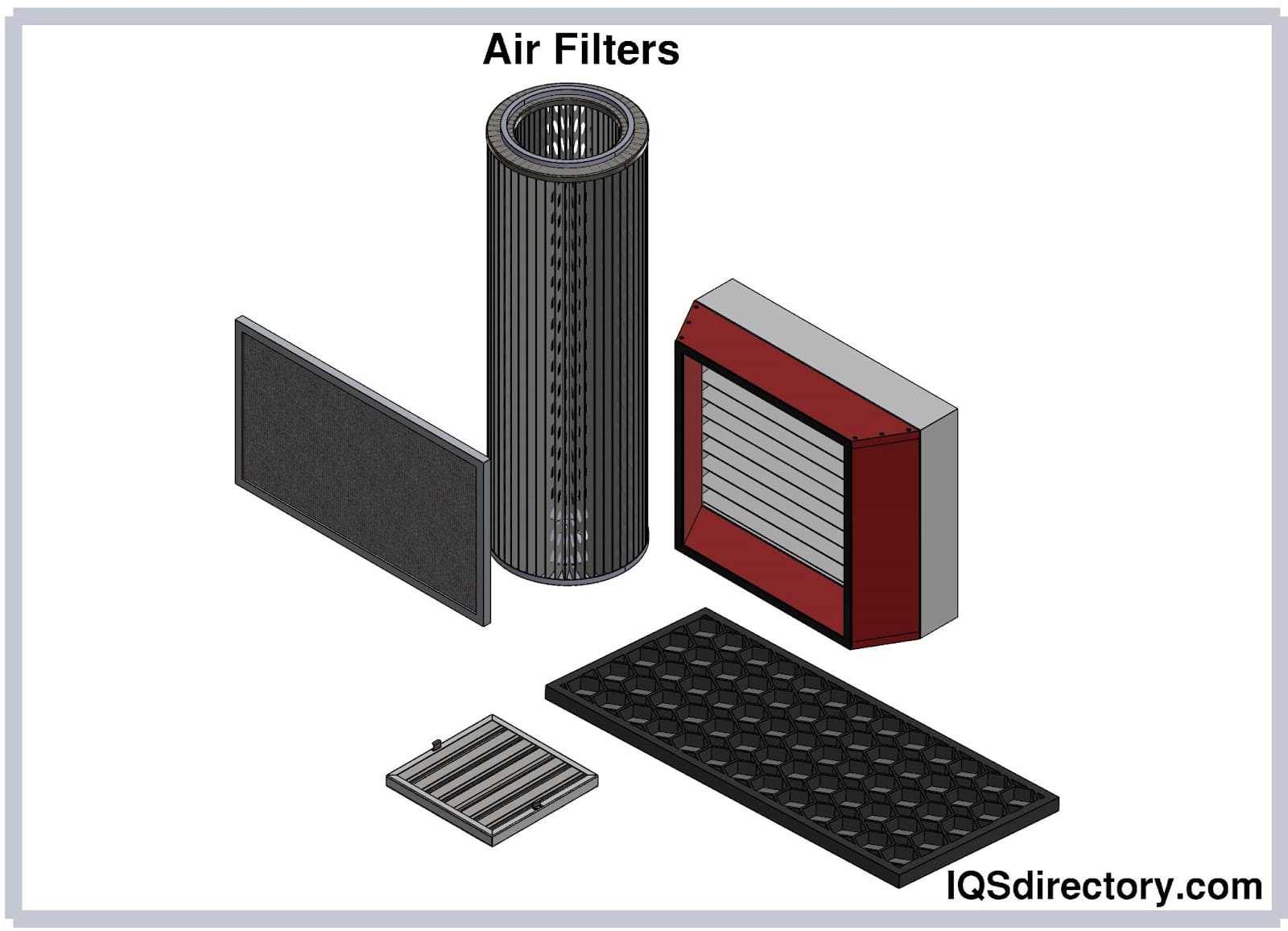

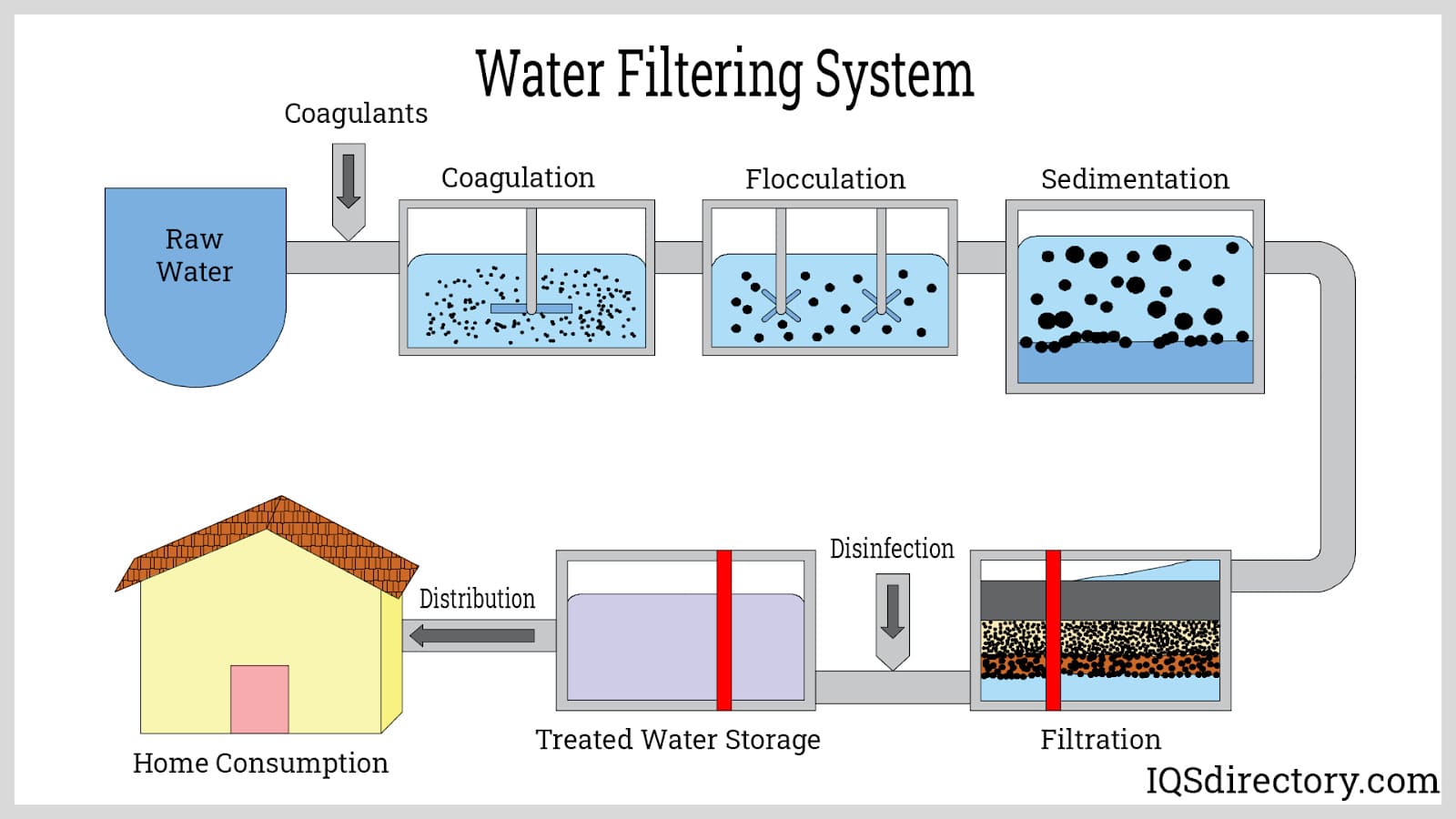


 Air Filters
Air Filters Liquid Filters
Liquid Filters Filtering Systems
Filtering Systems Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services